1. What are Data Structures?
A data structure is a mechanical or logical way that data is organized within a program. The organization of data is what determines how a program performs. There are many types of data structures, each with its own uses. When designing code, we need to pay particular attention to the way data is structured. If data isn't stored efficiently or correctly structured, then the overall performance of the code will be reduced.
2. Why Create Data Structures?
Data structures serve a number of important functions in a program. They ensure that each line of code performs its function correctly and efficiently, they help the programmer identify and fix problems with his/her code, and they help to create a clear and organized code base.
3. What are some applications of Data structures?
Following are some real-time applications of data structures:
4. Explain the process behind storing a variable in memory.
- A variable is stored in memory based on the amount of memory that is needed. Following are the steps followed to store a variable:
- The required amount of memory is assigned first.
- Then, it is stored based on the data structure being used.
- Using concepts like dynamic allocation ensures high efficiency and that the storage units can be accessed based on requirements in real-time.
5. Can you explain the difference between file structure and storage structure?
- File Structure: Representation of data into secondary or auxiliary memory say any device such as a hard disk or pen drives that stores data which remains intact until manually deleted is known as a file structure representation.
- Storage Structure: In this type, data is stored in the main memory i.e RAM, and is deleted once the function that uses this data gets completely executed.
The difference is that the storage structure has data stored in the memory of the computer system, whereas the file structure has the data stored in the auxiliary memory.
6. Describe the types of Data Structures?
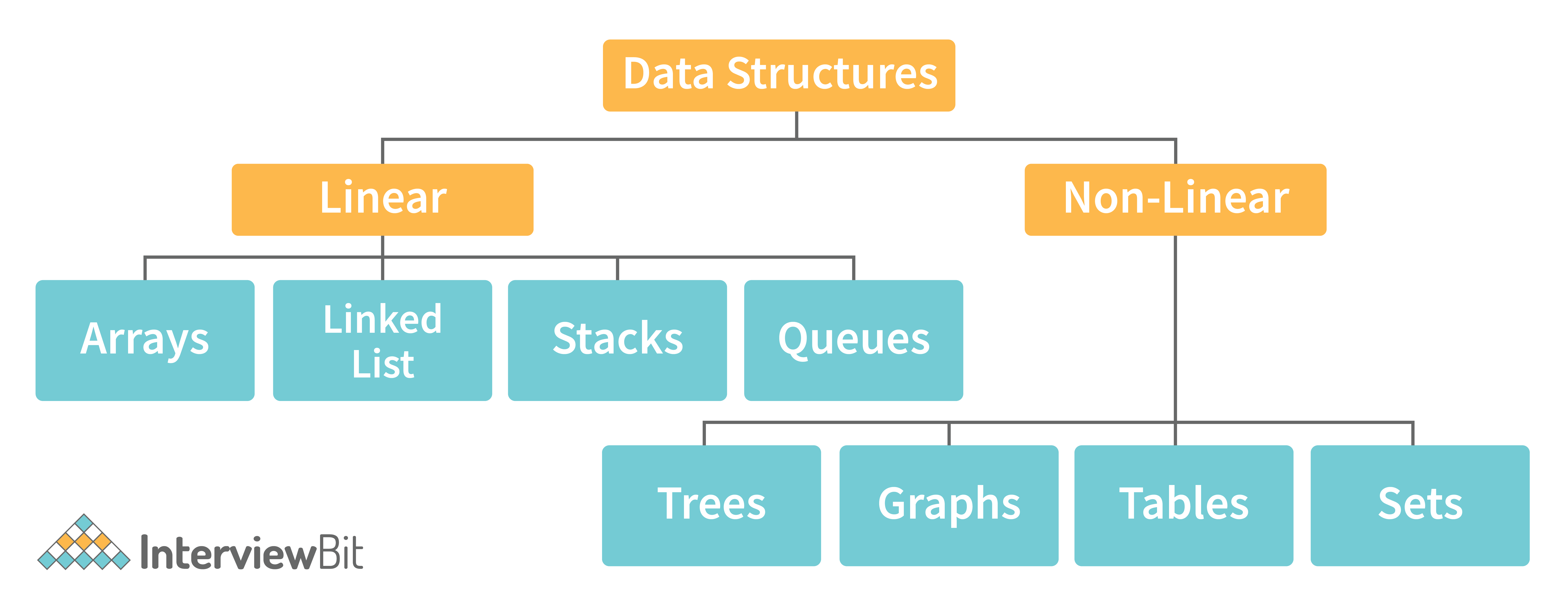
- Linear Data Structure: A data structure that includes data elements arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is connected to its previous and next nearest elements, is referred to as a linear data structure. Arrays and linked lists are two examples of linear data structures.
- Non-Linear Data Structure: Non-linear data structures are data structures in which data elements are not arranged linearly or sequentially. We cannot walk through all elements in one pass in a non-linear data structure, as in a linear data structure. Trees and graphs are two examples of non-linear data structures.
7. What is a stack data structure? What are the applications of stack?
A stack is a data structure that is used to represent the state of an application at a particular point in time. The stack consists of a series of items that are added to the top of the stack and then removed from the top. It is a linear data structure that follows a particular order in which operations are performed. LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out) are two possible orders. A stack consists of a sequence of items. The element that's added last will come out first, a real-life example might be a stack of clothes on top of each other. When we remove the cloth that was previously on top, we can say that the cloth that was added last comes out first.


This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletePost a Comment